Field Definitions: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'Tips for developers working within the Sysgem Enterprise Manager (SEM) environment'. | 'Tips for developers working within the Sysgem Enterprise Manager (SEM) environment'. | ||
---- | |||
''Finding your way around the SEM development Interface'' | ''Finding your way around the SEM development Interface'' | ||
'''Defining Fields in a SEM Input Form''' | |||
This section describes the the different type of fields on an input form and how to create them in a SEM library. | This section describes the the different type of fields on an input form and how to create them in a SEM library. | ||
| Line 252: | Line 255: | ||
--- | ---- | ||
* '''13. Size''' | * '''13. Size''' | ||
Latest revision as of 09:42, 24 February 2011
'Tips for developers working within the Sysgem Enterprise Manager (SEM) environment'.
Finding your way around the SEM development Interface
Defining Fields in a SEM Input Form
This section describes the the different type of fields on an input form and how to create them in a SEM library.
Use the ![]() icon at the top of the page to add new fields to the form. Double click on the field entry and the following field definition form is shown:
icon at the top of the page to add new fields to the form. Double click on the field entry and the following field definition form is shown:
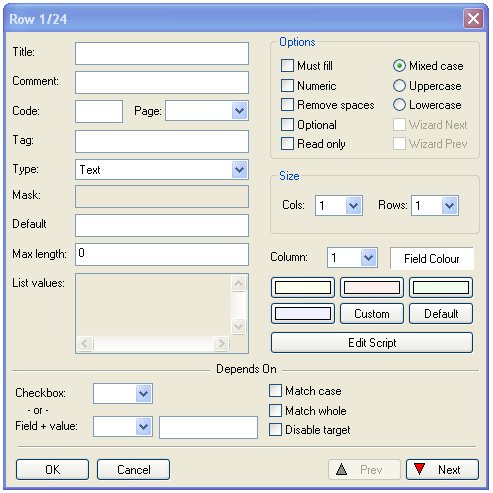
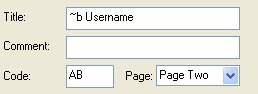
- 1. Title
The "Title" field can be preceded by the characters "~b" (to make the text bold).
e.g.
~B Username
If the field Type is going to be "- None -", then you can also use the "~o" prefix to fill the background with a grey fill colour and change the text colour to white.
e.g.
~o test123
Use the "~f" prefix in conjunction with the "~o" prefix, i.e. "~f~o" to broaden the grey band and to extend it to the outer edge of the form. This is appropriate for the first line heading on a form.
e.g.
~f~o test123
- 2. Comment
The comment field provides the text for a "Tooltip" when the cursor hovers over a Title field of an input form.
- 3. Code
The code field gives a two alpha-character unique code to the field. The code "SV" is reserved for the "Server" or "Agent" field. Scripts refer to the fields using this two character code, so for example the "Username" field may be given a code "UN" and a Perl script would access the content of this field via the variable: $INPUT_UN.
VMS DCL scripts would use the logical name: INPUT_UN, and UNIX Korn Shell scripts would refer to the variable as: ${INPUT_UN}.
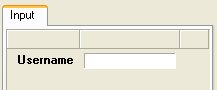
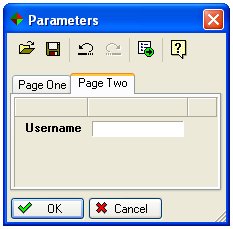
- 4. Page
The input form can be divided into pages by using tabs along the top edge of the form. A field is allocated to a particular page by entering a page name in the "Page" field.
e.g.
- 5. Tag
The Tag field allows the field on the input form to be referenced with something a bit more meaningful than the two character unique field code. For example, entering "USERNAME" in the tag field allows the input field to be referenced by $InputByTag{"USERNAME"} by the following scripts:
When a SEM display is started:
- Startup: Initialise
- Main Display Script: Pre-Processing
- Main Display Script: Post-Processing
When a menu option is invoked, before the input form is displayed:
- (M) Fields
After data has been entered into the input form:
- (M) Pre-Processing
- (M) Post-Processing
*** Please note: The Tag field is a candidate for being retired in a future version of the product and is not recommended for use.
- 6. Type
The Type field defines how the input field looks and behaves. For example, is it a simple text field, or is it a checkbox, or a pull down selection list?
Below is a full list of field types that are supported:
- Date (string)
- Date (seconds)
- Date / Time (VMS Format)
- Text
- Text (mask)
- Checkbox
- Colour Picker
- Filename (Open)
- Filename (Save)
- Folder
- List
- List (Editable)
- List (Fixed)
- List (multi-select)
- List (multi-select, single column)
- List (single select)
- Password (create)
- Password (input)
- Script button
- - none -
- Agent list
- Agent list (multi)
- Agent list (NT)
- Agent list (UNIX)
- Agent list (VMS)
- Agent list - All defs
- Agent list - All defs (multi-select)
- System DSNs
- 7. Mask
The Mask field is only relevant when the field type is "Text (Mask)". It permits the formatting f the text field so that only certain character type may be entered. This is particularly useful, for example if entering a Reference code that must always conform to a particular format and layout.
The following is a list of the permitted mask characters:
- # - keyed characters must be numbers only in this position
- ? - keyed characters must be alphabetical only in this position
- A - keyed characters must be alphanumerics only in this position
- L - keyed characters must be alphabets only, forced to lowercase in this position
- U - keyed characters must be alphabets only, forced to uppercase in this position
- & - keyed characters may be anything in this position
- Anything else will be treated as a literal. If any of the above characters are required as a literal then they must be escaped with a preceding "\" (backslash) character.
So for example:
UUU - ###### L
... will force the user to enter three uppercase alphabet characters in the first three character positions of the field (any lower case alphabets will be entered as uppercase equivalents). The cursor will then move automatically to the first numeric position. Numeric characters must then be entered for the next 6 keystrokes (anything else will be ignored). Finally a single lowercase alphabet character will complete the entry (an upper case character keyed in this position will be converted to its lower case equivalent).
- 8. Default
The Default field defines a value that will be automatically entered into the input field the first time it is displayed.
- 9. Max length
The Max length field defines the maximum number if characters that may be typed into the input field.
- 10. List values
The List values field is used to define the list of values that are shown as a pull down option list when the field type is one of the "List" field types. Double click in this field to start a text editor on the field, or simply type the list in the field using a <carriage return> to terminate each item.
- 11. List values
The List values field
- 12. Options
Options may be set as follows:
- Must Fill
- Numeric
- Remove spaces
- Optional
- Read only
- Mixed case / Upper case / Lower case
- 13. Size
The size of the field may be set in terms of the number of rows or the number of columns that the field occupies.
- 14. Column
The position of the field on the input can be pre-determined by setting the column number in this field. Column numbering starts at "1".
- 15. Field Colour
One of the preset field colours or a custom field colour may be used to determine the colour of the entry field. Fields of type "- none -" are transparent adopting the colour of the background.
- 16. Edit Script
If the field type is "Script button", then the field will appear as a Press button and the "Edit Script" option becomes available to enter a Perl script that will be executed whenever the button is pressed. Inside the script of such a field, the fields that have already been filled in are available to the script using the variables $INPUT_XX (where XX is the field code. The script also has the ability to output values into any field by using the following Perl statement:
print "XX : <new value>\n"; # where XX is the field code for the required field, and,
# "<new value>" is the text string that should be entered into the field.
- 17. Depends on
Any field in the form can be made dependent on another field. So for example, if a field is dependent on a a checkbox being selected "On", then the field code for the checkbox is selected in the drop down list of checkboxes. If a field is dependent on a checkbox being selected "Off", then the negated field code is selected (eg -AC). Similarly a field can be made dependent on a text value in another field. This is also entered in this section of the field definition form.