Access Control Tokens
'Tips for developers working within the Sysgem Enterprise Manager (SEM) environment'.
Permissions available to a SEM User for features within a SEM Module
Access Control Tokens
A SEM Module can have certain features made available to, or denied to, a user by use of "Access Control Token Settings"
- Use the SEM menu option: "Managers" > "SEM Users" > "Tokens" to set the correct settings on a token.
- Use the SEM menu option: "Managers" > "SEM Users" > "Profiles" to assign a token to a Profile.
- Use the SEM menu option: "Managers" > "SEM Users" > "Accounts" to assign a Profile to a SEM User.
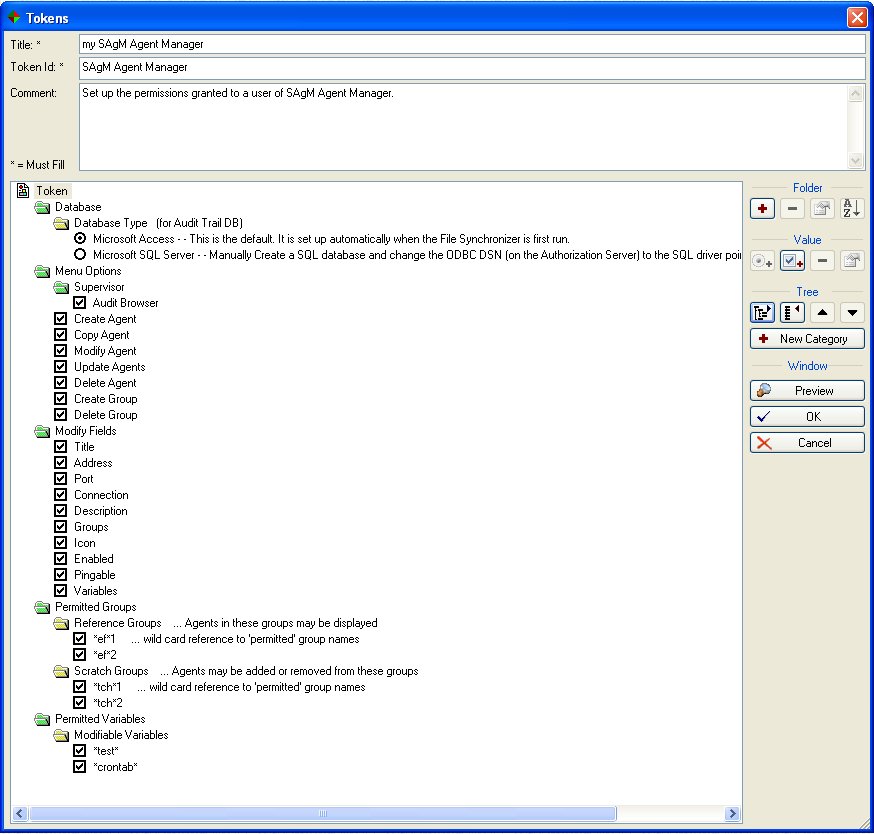
Below is a screenshot of the Access Control Token for the SAgM Module:
Reading Access Control Token Settings from within a Workstation Script
Details of the "Access Control Tokens" that are available to the SEM Users (via the SEM Profile for this user) are available to all scripts that run on the SEM user's workstation.
If a script requires the Access Control Token Settings, then the following comment lines need to be added to the script that runs on the workstation:
#
# @{{INCLUDE_TOKENS
#
.... this will result in the following associative array being defined by the SEM framework when the script is invoked:
my %UserTokens = ();
#
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Database Type"}}, "Microsoft Access");
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Audit Browser"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Create Agent"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Copy Agent"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Modify Agent"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Update Agents"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Delete Agent"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Create Group"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Delete Group"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Title"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Address"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Port"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Connection"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Description"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Groups"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Icon"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Enabled"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Pingable"} = 1;
$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Variables"} = 1;
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Reference Groups"}}, "\*ef\*1");
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Reference Groups"}}, "\*ef\*2");
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Scratch Groups"}}, "\*tch\*1");
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Scratch Groups"}}, "\*tch\*2");
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Modifiable Variables"}}, "\*test\*");
push(@{$UserTokens{"SAgM Agent Manager"}{"Modifiable Variables"}}, "\*crontab\*"
If Token settings are required by a script that runs on an agent, then the token settings need to be read first by the "(M) Pre-processing" script (using the above technique) and then made available to the SEM Agent script by using the "ADD_SVR from a menu Pre-Process" technique.